The Urban Environment
Photos by Jack Lueders-Booth

Urbanization has transformed Latin America over the last forty years. Its cities, always diverse and lively, have now also become chaotic and centers of social conflict. Millions of subsistence farmers and rural townsfolk have suddenly turned into metropolitan inhabitants, their lives influenced more by the ebb and flow of a global economy than by the rhythms of the agricultural harvest.
Zones unfit for human habitation have become a prominent feature of the physical urban landscape. Many of these places suffer from an obvious proximity to industrial wastes, or run high probabilities of disasters such as flooding and landslides, or themselves present a danger to sensitive ecological areas such as water supply and endangered microclimates. People like the Tijuana pepineros in these dramatic photos by Jack Lueders-Booth must live as they can, with resourcefulness their greatest ally.
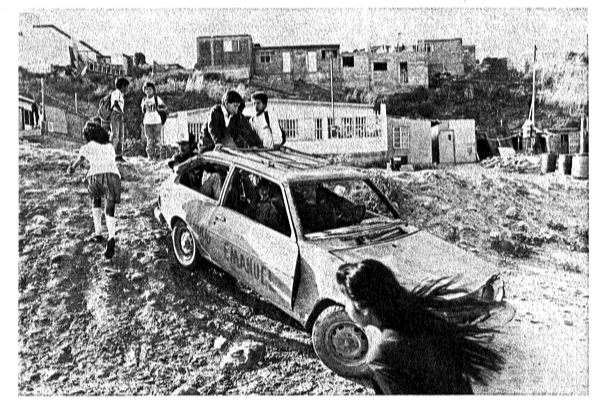
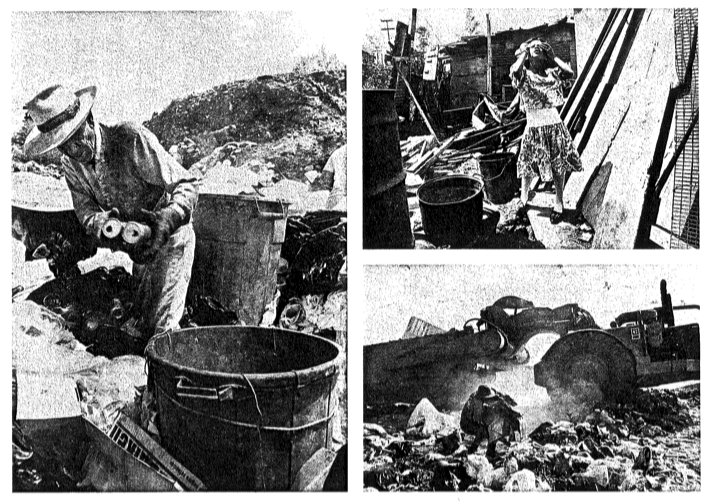

Jack Lueders-Booth’s photographs were featured in the Center’s first Latin American and Latino Art Forum in the fall of 1997. His work has been supported by the National Endowment for the Arts, the Library of Congress, and the Smithsonian Institute. He continues to create a photo- graphic commentary on what it means to survive in and off of the dumps in a bustling border city.
The terrible irony is that such people depend on their deficient environment all the more for livelihood, since they often appropriate and give new value to runoff water, unused land, and ever other people’s garbage through their labor.
This may be one extreme. However, uncounted millions throughout Latin America, many of them in the working or middle class, acquire their land ‘illegally’ as squatters because of the prohibitive cost and inaccessibility of land. The wealthy, while not called squatters, may ‘develop’ exclusive settlements at the margin of the law, often in beautiful but fragile natural settings at the periphery of the city, sometimes even in national parks. The authorities in many countries have all but acceded to laissez-faire as a method of land distribution, to corporations as well as individuals.
Because of the special problems created by urban areas, many people instinctively view the city as “not-natural”, or “outside the environment”. However, the dichotomy between man and nature is misleading. The city is the immediate environment for urbanites, whose public health depends in large measure on environmental health. Additionally, human beings consume resources and expel waste, making us part of a larger natural system on the regional and even global level. We are never truly outside the environment.
Fall 1998
Andre Leroux, while a staff member of DRCLAS, pursues completion of his Master’s in Urban and Environmental Studies from El Colegio de Mexico in Mexico City, where he lived from 1995-1997. His thesis deals with environmental impact assessment in Mexico.
Jack Lueders-Booth is the photography administrator and Tutor in Visual and Environmental Studies at Harvard’s Carpenter Center.
Related Articles
Environment, Indians, and Oil
An Indian leader from the Upper Amazon recently commented to me that the whole issue of the environment, Indians, and oil companies had taken on global mythical proportions. He was partly…
El Salvador Challenge
Over the past few years, El Salvador has accomplished what can only be described as a political and economic miracle. Peace accords were concluded, ending a decade-long destructive civil…
Ecology, Art, and Home
Growing up in the Argentine Pampas gave me a great appreciation for even the simplest materials. As a little girl, I would sit in the dirt of the sun-scorched patio and admire the plain dirt…




